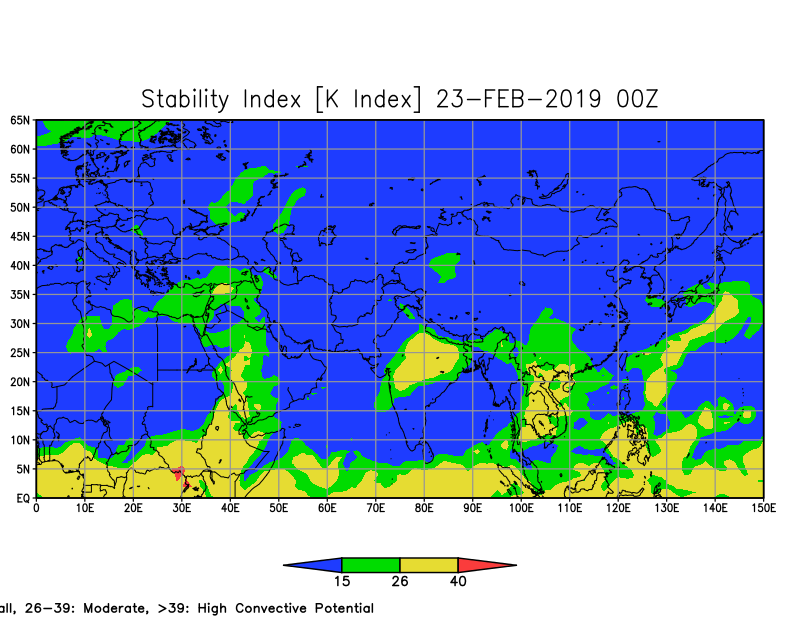
The K-Index or George's Index is a measure of thunderstorm potential in meteorology. According to the National Weather Service, the index harnesses measurements such as "vertical temperature lapse rate, moisture content of the lower atmosphere, and the vertical extent of the moist layer." It was developed by the American meteorologist Joseph J. George, and published in the 1960 book Weather Forecasting for Aeronautics.
Definition
The index is derived arithmetically by:
Where :
- = Dew point at 850 hPa
- = Temperature at 850 hPa
- = Dew point at 700 hPa
- = Temperature at 700 hPa
- = Temperature at 500 hPa
Interpretation
The K Index is related to the probability of occurrence of a thunderstorm. It was developed with the idea that Potential = 4 x (KI - 15), which gives the following interpretation:
References